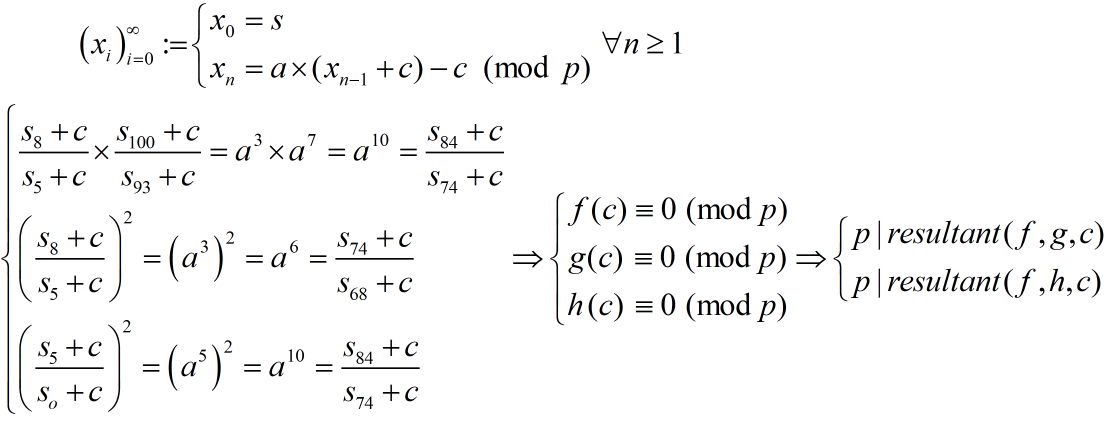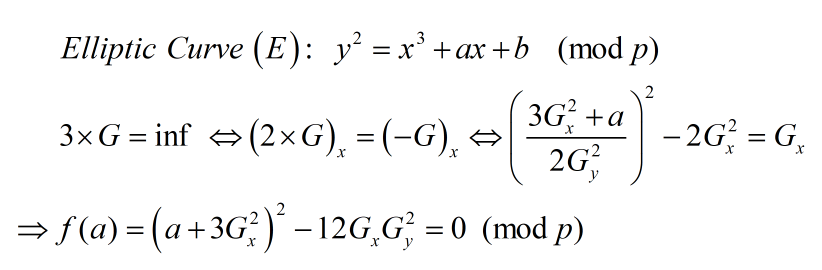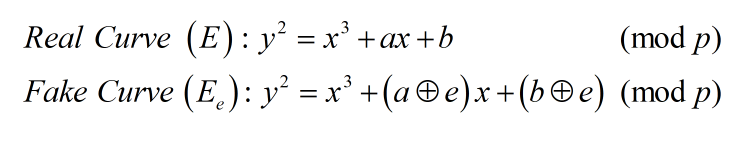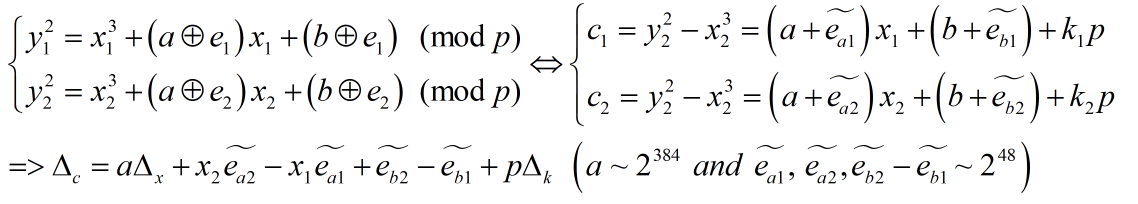tadpole (261 solves 109 points)
Description
tadpoles only know the alphabet up to b… how will they ever know what p is?Attachmets
tadpole.py output.txt
Challenge overview
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long, isPrime
from secrets import randbelow
p = bytes_to_long(open("flag.txt", "rb").read())
assert isPrime(p)
a = randbelow(p)
b = randbelow(p)
def f(s):
return (a * s + b) % p
print("a = ", a)
print("b = ", b)
print("f(31337) = ", f(31337))
print("f(f(31337)) = ", f(f(31337)))
1
2
3
4
# a = 7904681699700731398014734140051852539595806699214201704996640156917030632322659247608208994194840235514587046537148300460058962186080655943804500265088604049870276334033409850015651340974377752209566343260236095126079946537115705967909011471361527517536608234561184232228641232031445095605905800675590040729
# b = 16276123569406561065481657801212560821090379741833362117064628294630146690975007397274564762071994252430611109538448562330994891595998956302505598671868738461167036849263008183930906881997588494441620076078667417828837239330797541019054284027314592321358909551790371565447129285494856611848340083448507929914
# f(31337) = 52926479498929750044944450970022719277159248911867759992013481774911823190312079157541825423250020665153531167070545276398175787563829542933394906173782217836783565154742242903537987641141610732290449825336292689379131350316072955262065808081711030055841841406454441280215520187695501682433223390854051207100
# f(f(31337)) = 65547980822717919074991147621216627925232640728803041128894527143789172030203362875900831296779973655308791371486165705460914922484808659375299900737148358509883361622225046840011907835671004704947767016613458301891561318029714351016012481309583866288472491239769813776978841785764693181622804797533665463949
Đề cho ta 2 số $a, b$ và hàm $f(x) = ax + b \in \mathbb{F}_{p}$ với $p$ là số nguyên tố cũng chính là flag cần tìm, ngoài ra ta còn biết thêm hai giá trị là $f(31337)$ và $f\left(f(31337)\right)$.
Solution
Ta thấy ngay tìm $p$ bằng phép tính đơn giản:
\[p = \gcd\left(f(31337) - 31337, f\left(f(31337)\right) - f(31337)\right)\]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
from Crypto.Util.number import *
a = 7904681699700731398014734140051852539595806699214201704996640156917030632322659247608208994194840235514587046537148300460058962186080655943804500265088604049870276334033409850015651340974377752209566343260236095126079946537115705967909011471361527517536608234561184232228641232031445095605905800675590040729
b = 16276123569406561065481657801212560821090379741833362117064628294630146690975007397274564762071994252430611109538448562330994891595998956302505598671868738461167036849263008183930906881997588494441620076078667417828837239330797541019054284027314592321358909551790371565447129285494856611848340083448507929914
f = 52926479498929750044944450970022719277159248911867759992013481774911823190312079157541825423250020665153531167070545276398175787563829542933394906173782217836783565154742242903537987641141610732290449825336292689379131350316072955262065808081711030055841841406454441280215520187695501682433223390854051207100
ff = 65547980822717919074991147621216627925232640728803041128894527143789172030203362875900831296779973655308791371486165705460914922484808659375299900737148358509883361622225046840011907835671004704947767016613458301891561318029714351016012481309583866288472491239769813776978841785764693181622804797533665463949
p = GCD(a*31337 + b - f, a*f + b - ff)
assert isPrime(p)
flag = long_to_bytes(p)
print(flag)
Flag:
corctf{1n_m4th3m4t1c5,_th3_3ucl1d14n_4lg0r1thm_1s_4n_3ff1c13nt_m3th0d_f0r_c0mput1ng_th3_GCD_0f_tw0_1nt3g3rs}
luckyguess (148 solves 118 points)
Description
i hope you’re feeling lucky today
nc be.ax 31800Attachmets
luckyguess.py
Challenge overview
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
#!/usr/local/bin/python
from random import getrandbits
p = 2**521 - 1
a = getrandbits(521)
b = getrandbits(521)
print("a =", a)
print("b =", b)
try:
x = int(input("enter your starting point: "))
y = int(input("alright, what's your guess? "))
except:
print("?")
exit(-1)
r = getrandbits(20)
for _ in range(r):
x = (x * a + b) % p
if x == y:
print("wow, you are truly psychic! here, have a flag:", open("flag.txt").read())
else:
print("sorry, you are not a true psychic... better luck next time")
Đề cho ta tham số của hàm LCG, để lấy được flag ta phải nhập cùng lúc hai giá trị: giá trị đầu tiên $x$ sẽ là giá trị khởi tạo cho LCG, giá trị tiếp theo $y$ phải đúng bằng giá trị output thứ $r$ của hàm LCG (với $r$ là số random bởi server)
Solution
Phân tích tới đây ta nghĩ ngay tới việc tìm điểm bất động của hàm số, cụ thể là tìm $x_{o}$ sao cho:
\[\begin{align*} x_{o} &\equiv ax_{o} + b &\pmod{p} \\ \Leftrightarrow x_{o} &\equiv \dfrac{b}{1 - a} &\pmod{p} \end{align*}\]Vậy ta chỉ việc gửi cặp số $(x, y) = (x_{o}, x_{o})$ thì dù cho server có random ra $r$ bao nhiêu đi nữa, kết quả tính vẫn bằng nhau!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
from pwn import *
from Crypto.Util.number import *
p = 2**521 - 1
def fixed_point(a, b):
return b * inverse(1 - a, p) % p
io = remote("be.ax", 31800)
a = int(io.recvline()[4:])
b = int(io.recvline()[4:])
x = fixed_point(a, b)
io.recvuntil(b'enter your starting point: ')
io.sendline(str(x).encode())
io.recvuntil(b'alright, what\'s your guess? ')
io.sendline(str(x).encode())
print(io.recvline())
Flag:
corctf{r34l_psych1c5_d0nt_n33d_f1x3d_p01nt5_t0_tr1ck_th15_lcg!}
exchanged (93 solves, 131 points)
Description
you could make an exchange out of thisAttachmets
exchanged.py output.txt
Challenge overview
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad
from hashlib import sha256
from secrets import randbelow
p = 142031099029600410074857132245225995042133907174773113428619183542435280521982827908693709967174895346639746117298434598064909317599742674575275028013832939859778024440938714958561951083471842387497181706195805000375824824688304388119038321175358608957437054475286727321806430701729130544065757189542110211847
a = randbelow(p)
b = randbelow(p)
s = randbelow(p)
print("p =", p)
print("a =", a)
print("b =", b)
print("s =", s)
a_priv = randbelow(p)
b_priv = randbelow(p)
def f(s):
return (a * s + b) % p
def mult(s, n):
for _ in range(n):
s = f(s)
return s
A = mult(s, a_priv)
B = mult(s, b_priv)
print("A =", A)
print("B =", B)
shared = mult(A, b_priv)
assert mult(B, a_priv) == shared
flag = open("flag.txt", "rb").read()
key = sha256(long_to_bytes(shared)).digest()[:16]
iv = long_to_bytes(randint(0, 2**128))
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv=iv)
print(iv.hex() + cipher.encrypt(pad(flag, 16)).hex())
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
p = 142031099029600410074857132245225995042133907174773113428619183542435280521982827908693709967174895346639746117298434598064909317599742674575275028013832939859778024440938714958561951083471842387497181706195805000375824824688304388119038321175358608957437054475286727321806430701729130544065757189542110211847
a = 118090659823726532118457015460393501353551257181901234830868805299366725758012165845638977878322282762929021570278435511082796994178870962500440332899721398426189888618654464380851733007647761349698218193871563040337609238025971961729401986114391957513108804134147523112841191971447906617102015540889276702905
b = 57950149871006152434673020146375196555892205626959676251724410016184935825712508121123309360222777559827093965468965268147720027647842492655071706063669328135127202250040935414836416360350924218462798003878266563205893267635176851677889275076622582116735064397099811275094311855310291134721254402338711815917
s = 35701581351111604654913348867007078339402691770410368133625030427202791057766853103510974089592411344065769957370802617378495161837442670157827768677411871042401500071366317439681461271483880858007469502453361706001973441902698612564888892738986839322028935932565866492285930239231621460094395437739108335763
A = 27055699502555282613679205402426727304359886337822675232856463708560598772666004663660052528328692282077165590259495090388216629240053397041429587052611133163886938471164829537589711598253115270161090086180001501227164925199272064309777701514693535680247097233110602308486009083412543129797852747444605837628
B = 132178320037112737009726468367471898242195923568158234871773607005424001152694338993978703689030147215843125095282272730052868843423659165019475476788785426513627877574198334376818205173785102362137159225281640301442638067549414775820844039938433118586793458501467811405967773962568614238426424346683176754273
e0364f9f55fc27fc46f3ab1dc9db48fa482eae28750eaba12f4f76091b099b01fdb64212f66caa6f366934c3b9929bad37997b3f9d071ce3c74d3e36acb26d6efc9caa2508ed023828583a236400d64e
Nhìn sơ qua đề bài thì ta thấy nó giống Diffie-Hellman nhưng được thực hiện bằng …LCG
\[\left(x_{i}\right)^{\infty}_{i=0} := \begin{cases} x_{0} = s \\ x_{n} = ax_{n - 1} + b \pmod{p} \end{cases} \quad \forall n \ge 1\]Alice và Bob mỗi người có một cặp public - private key là $(d_{A}, x_{d_{A}})$ và $(d_{B}, x_{d_{B}})$, khi đó shared secret key sẽ là $x_{d_{A} + d_{B}}$. shared key sẽ được dùng làm AES-key để encrypt flag.
Solution
Rõ ràng ta cần tìm shared secret key từ $x_{d_{A}}$ và $x_{d_{B}}$. Ta thử biến đổi một chút… đặt:
\[c = \dfrac{b}{a - 1} \Rightarrow \dfrac{x_{n} + c}{x_{0} + c} = a^{n}\]Khi đó:
\[\dfrac{x_{d_{A} + d_{B}} + c}{x_{d_{A}} + c} = a^{d_{B}} = \dfrac{x_{d_{B}} + c}{x_{0} + c} \Rightarrow x_{d_{A} + d_{B}} = \dfrac{(x_{d_{A}} + c)(x_{d_{B}} + c)}{s + c} - c \pmod{p}\]Có key rồi ta decrypt AES nữa là có flag thui ~~
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import unpad
from hashlib import sha256
p = 142031099029600410074857132245225995042133907174773113428619183542435280521982827908693709967174895346639746117298434598064909317599742674575275028013832939859778024440938714958561951083471842387497181706195805000375824824688304388119038321175358608957437054475286727321806430701729130544065757189542110211847
a = 118090659823726532118457015460393501353551257181901234830868805299366725758012165845638977878322282762929021570278435511082796994178870962500440332899721398426189888618654464380851733007647761349698218193871563040337609238025971961729401986114391957513108804134147523112841191971447906617102015540889276702905
b = 57950149871006152434673020146375196555892205626959676251724410016184935825712508121123309360222777559827093965468965268147720027647842492655071706063669328135127202250040935414836416360350924218462798003878266563205893267635176851677889275076622582116735064397099811275094311855310291134721254402338711815917
s = 35701581351111604654913348867007078339402691770410368133625030427202791057766853103510974089592411344065769957370802617378495161837442670157827768677411871042401500071366317439681461271483880858007469502453361706001973441902698612564888892738986839322028935932565866492285930239231621460094395437739108335763
A = 27055699502555282613679205402426727304359886337822675232856463708560598772666004663660052528328692282077165590259495090388216629240053397041429587052611133163886938471164829537589711598253115270161090086180001501227164925199272064309777701514693535680247097233110602308486009083412543129797852747444605837628
B = 132178320037112737009726468367471898242195923568158234871773607005424001152694338993978703689030147215843125095282272730052868843423659165019475476788785426513627877574198334376818205173785102362137159225281640301442638067549414775820844039938433118586793458501467811405967773962568614238426424346683176754273
enc = bytes.fromhex("e0364f9f55fc27fc46f3ab1dc9db48fa482eae28750eaba12f4f76091b099b01fdb64212f66caa6f366934c3b9929bad37997b3f9d071ce3c74d3e36acb26d6efc9caa2508ed023828583a236400d64e")
c = b * inverse(a - 1, p) % p
shared = ((A + c) * (B + c) * inverse(s + c, p) - c) % p
key = sha256(long_to_bytes(shared)).digest()[:16]
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv=enc[:16])
flag = unpad(cipher.decrypt(enc[16:]), 16)
print(flag)
Flag:
corctf{th1s_lcg_3xch4ng3_1s_4_l1ttl3_1ns3cur3_f0r_n0w}
hidE (88 solves, 133 points)
Description
This RSA encryption service is so secure we’re not even to tell you how we encrypted it
nc be.ax 31124Attachmets
hidE.py
Challenge overview
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
import random
import time
import math
import binascii
from Crypto.Util.number import *
p, q = getPrime(512), getPrime(512)
n = p * q
phi = (p - 1) * (q - 1)
flag = open('../flag.txt').read().encode()
random.seed(int(time.time()))
def encrypt(msg):
e = random.randint(1, n)
while math.gcd(e, phi) != 1:
e = random.randint(1, n)
pt = bytes_to_long(msg)
ct = pow(pt, e, n)
return binascii.hexlify(long_to_bytes(ct)).decode()
def main():
print('Secure Encryption Service')
print('Your modulus is:', n)
while True:
print('Options')
print('-------')
print('(1) Encrypt flag')
print('(2) Encrypt message')
print('(3) Quit')
x = input('Choose an option: ')
if x not in '123':
print('Unrecognized option.')
exit()
elif x == '1':
print('Here is your encrypted flag:', encrypt(flag))
elif x == '2':
msg = input('Enter your message in hex: ')
print('Here is your encrypted message:', encrypt(binascii.unhexlify(msg)))
elif x == '3':
print('Bye')
exit()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Đề cho ta truy cập vào RSA encryption Oracle, ở đây ta biết RSA modulus $n$ và có thể encrypt tùy ý (kể cả flag). Điều thú vị ở đây là ta không được biết public exponent $e$ và $e$ lại được random với seed là current time.
Solution
Để ý rằng mặc dù chúng ta không biết $e$ nhưng hoàn toàn có thể brute force seed (current time + $\Delta_{t}$ - khoảng thời gian lệch do kết nối tới server). Có $e$ rồi ta dùng common modulus attack để tìm flag:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
from sage.all import *
from pwn import *
from Crypto.Util.number import *
import random
import time
import math
from itertools import combinations
def rnd(s):
E = []
for i in range(-1, 3):
random.seed(s + i)
for _ in range(2):
e = random.randint(1, n)
while math.gcd(e, 2) != 1:
e = random.randint(1, n)
E.append(e)
return E
def getencflag():
io.recvuntil(b'Choose an option: ')
io.sendline(b'1')
io.recvuntil(b'Here is your encrypted flag: ')
return int(io.recvline()[:-1].decode(), 16)
io = remote("be.ax", 31124)
io.recvline()
io.recvuntil(b'Your modulus is: ')
n = int(io.recvline())
seed = int(time.time())
c1 = getencflag()
c2 = getencflag()
E = rnd(seed)
for (e1, e2) in combinations(E, 2):
_, u, v = xgcd(e1, e2)
flag = long_to_bytes(int(pow(c1, u, n) * pow(c2, v, n) % n))
if b'corctf{' in flag:
print(f'[+] Flag: {flag}')
break
Flag:
corctf{y34h_th4t_w4snt_v3ry_h1dd3n_tbh_l0l}
generous (49 solves, 163 points)
Description
Let me introduce you to this nice oracle i found…
nc be.ax 31244Attachments
generous.py
Challenge overview
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
from Crypto.Util.number import getPrime, inverse, bytes_to_long
from random import randrange
with open("flag.txt", "rb") as f:
flag = f.read().strip()
def gen_keypair():
p, q = getPrime(512), getPrime(512)
n = (p**2) * q
while True:
g = randrange(2, n)
if pow(g, p-1, p**2) != 1:
break
h = pow(g, n, n)
return (n, g, h), (g, p, q)
def encrypt(pubkey, m):
n, g, h = pubkey
r = randrange(1, n)
c = pow(g, m, n) * pow(h, r, n) % n
return c
def decrypt(privkey, c):
g, p, q = privkey
a = (pow(c, p-1, p**2) - 1) // p
b = (pow(g, p-1, p**2) - 1) // p
m = a * inverse(b, p) % p
return m
def oracle(privkey, c):
m = decrypt(privkey, c)
return m % 2
pub, priv = gen_keypair()
n, g, h = pub
print(f"Public Key:\n{n = }\n{g = }\n{h = }")
print(f"Encrypted Flag: {encrypt(pub, bytes_to_long(flag))}")
while True:
inp = int(input("Enter ciphertext> "))
print(f"Oracle result: {oracle(priv, inp)}")
Đọc qua cách encrypt và decrypt thì mình quát hiện đây là Okamoto–Uchiyama cryptosystem, ta chú ý một tính chất thú vị sau
Bài này biết được bộ public key $(n, g, h)$, vậy ta có thể tự encrypt được. Hơn nữa ta cũng được phép decrypt nhưng chỉ biết được bit cuối của kết quả (LSB oracle), vậy ta thử sử dụng tính chất homomorphic và LSB oracle để khai thác thông tin từ flag:
Khi đó
\[\begin{align*} oracle\left(encrypt(flag) \times encrypt(-2^{i})\right) &= \left((flag - 2^{i}) \pmod{p} \right) \pmod{2} \\ &= \begin{cases} \text{0 if flag} < 2^{i} \\ \text{1 if flag} > 2^{i} \end{cases} \quad \text{(flag is odd)} \end{align*}\]Từ đó ta hoàn toàn brute được từng bit của flag
Solution
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
from pwn import *
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from random import randrange
def orc(enc):
io.recvuntil(b"Enter ciphertext> ")
io.sendline(str(enc).encode())
io.recvuntil(b'Oracle result: ')
return int(io.recvline())
def encrypt(pubkey, m):
n, g, h = pubkey
r = randrange(1, n)
c = pow(g, m, n) * pow(h, r, n) % n
return c
io = remote("be.ax", 31244)
io.recvline()
n = int(io.recvline()[4:])
g = int(io.recvline()[4:])
h = int(io.recvline()[4:])
io.recvuntil(b'Encrypted Flag: ')
c = int(io.recvline())
pub = (n, g, h)
# flag bits...
flag = 2**318 + 1
for i in range(317, -1, -1):
guess_flag = flag + 2**i
if 1 == orc(c * encrypt(pub, -guess_flag)%n):
flag = guess_flag
print(f'[+] Flag: {long_to_bytes(flag)}')
Flag:
corctf{see?1_bit_is_very_generous_of_me}
leapfrog (36 solves, 186 points)
Attachments
leapfrog.py output.txt
Challenge overview
Lại là LCG, nhưng lần này khó ăn hơn…
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes, getPrime
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad
from hashlib import sha256
from secrets import randbelow
from random import sample
p = getPrime(256)
a = randbelow(p)
b = randbelow(p)
s = randbelow(p)
def f(s):
return (a * s + b) % p
jumps = sample(range(3, 25), 12)
output = [s]
for jump in jumps:
for _ in range(jump):
s = f(s)
output.append(s)
print(jumps)
print(output)
flag = open("flag.txt", "rb").read()
key = sha256(b"".join([long_to_bytes(x) for x in [a, b, p]])).digest()[:16]
iv = long_to_bytes(randbelow(2**128))
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv=iv)
print(iv.hex() + cipher.encrypt(pad(flag, 16)).hex())
1
2
3
[5, 3, 23, 13, 24, 6, 10, 9, 7, 4, 19, 16]
[26242498579536691811055981149948736081413123636643477706015419836101346754443, 30320412755241177141099565765265147075632060183801443609889236855980299685595, 65684356693401962957802832810273549345608027337432965824937963429120291339333, 15025547765549333168957368149177848577882555487889680742466312084547650972663, 46764069432060214735440855620792051531943268335710103593983788232446614161424, 71575544531523096893697176151110271985899529970263634996534766185719951232899, 8149547548198503668415702507621754973088994278880874813606458793607866713778, 12081871161483608517505346339140143493132928051760353815508503241747142024697, 65627056932006241674763356339068429188278123434638526706264676467885955099667, 23413741607307309476964696379608864503970503243566103692132654387385869400762, 56014408298982744092873649879675961526790332954773022900206888891912862484806, 77000766146189604405769394813422399327596415228762086351262010618717119973525, 14589246063765426640159853561271509992635998018136452450026806673980229327448]
05ac5b17c67bcfbf5c43fa9d319cfc4c62ee1ce1ab2130846f776e783e5797ac1c02a34045e4130f3b8111e57397df344bd0e14f3df4f1a822c43c7a89fd4113f9a7702b0b0e0b0473a2cbac25e1dd9c
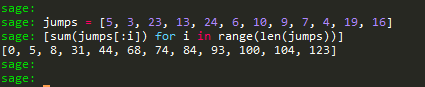
Nhiệm vụ của ta là tìm lại các tham số a, b, p từ các output được leak theo tự ngẫu nhiên của hàm LCG. Đầu tiên ta tính “vị trí” của các số được leak đối với output của hàm LCG.
recovering p
Ta thử xây dựng các đẳng thức liên hệ giữa các output được leak…
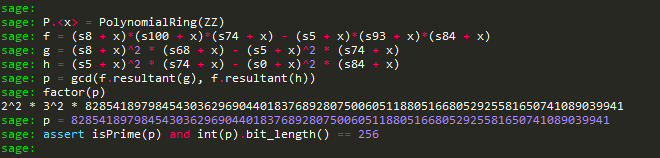
từ các đẳng thức vừa tìm được, dễ dàng tìm được p…
recovering a and b
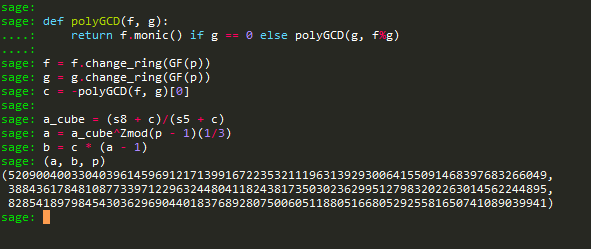
Có được p ta dễ dàng tìm được c từ đó dễ dàng tìm được a và b…
Solution
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import unpad
from hashlib import sha256
enc = bytes.fromhex("05ac5b17c67bcfbf5c43fa9d319cfc4c62ee1ce1ab2130846f776e783e5797ac1c02a34045e4130f3b8111e57397df344bd0e14f3df4f1a822c43c7a89fd4113f9a7702b0b0e0b0473a2cbac25e1dd9c")
a = 52090040033040396145969121713991672235321119631392930064155091468397683266049
b = 38843617848108773397122963244804118243817350302362995127983202263014562244895
p = 82854189798454303629690440183768928075006051188051668052925581650741089039941
key = sha256(b"".join([long_to_bytes(x) for x in [a, b, p]])).digest()[:16]
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv=enc[:16])
flag = unpad(cipher.decrypt(enc[16:]), 16)
print(f'[+] Flag: {flag}')
Flag:
corctf{:msfrog:_is_pr0ud_0f_y0ur_l34pfr0gg1ng_4b1lit135}
threetreasures (19 solves, 251 points)
Description
Let’s find the treasures of three amongst the order of three.Attachments
source.py output.txt
Challenge overview
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
from sage.all import *
from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long, getPrime
from random import getrandbits
from secret import flag, p, x, y
def random_pad(n, length):
return (n << (length - n.bit_length())) + getrandbits(length - n.bit_length())
flag = bytes_to_long(flag)
fbits = flag.bit_length()
piece_bits = fbits // 3
a, b, c = flag >> (2 * piece_bits), (flag >> piece_bits) % 2**piece_bits, flag % 2**piece_bits
print(a, b, c)
print(f'flag bits: {fbits}')
assert p.bit_length() == 512
q = getPrime(512)
n = p * q
ct = pow(random_pad(c, 512), 65537, n)
E = EllipticCurve(GF(p), [a, b])
G = E(x, y)
assert G * 3 == E(0, 1, 0)
print(f"n = {n}")
print(f"ct = {ct}")
print(f"G = {G}")
1
2
3
4
flag bits: 375
n = 97915144495462666300795364589570761584322186881492143950078938328867290046424857019504657598883431857075772605985768551863478086544857915637724181292135280539943713583281151707224031808445390796342632369109562433275679473233398168787639940620683354458292117457239552762694657810883738834935391913698852811737
ct = 20363336204536918055183609604474634074539942561101208682977506918349108499764147141944713060658857301108876346227077713201766486360148051069618774935469969057808945271860025712869868421279488925632657486125211168314387620225601572070169746014988350688548088791906161773656057212229972967244998930356157725393
G = (3115938227771961657567351113281194074601897467086373590156577019504528350118731801249444974253028485083440228959842232653488953448859690520619223338133881 : 2665631524518629436093690344927156713668794128141943350227439039472817541262750706395352700109556004195261826476428128993836186741129487842876154876730189 : 1)
Đọc sơ qua thì flag được chặt làm 3 khúc $a, b, c$ (mỗi phần 125 bits), $c$ được mã hóa bằng RSA còn $a, b$ lấy làm tham số cho EllipticCurve. Vậy ta cần xử lý thằng ECC trước, tìm ra $(a, b, p)$ có $p$ thì dễ dàng tìm được $c$
Ta được biết thêm tọa độ của điểm $G$ thuộc Curve, điều thú vị là order của nó bằng $3$
Vậy ta đã thiết lập được phương trình nhận $a$ làm nghiệm theo modulus $p$. Để ý $a$ có 125 bits (thậm chí ta còn biết thêm một số bits đầu của $a$ do flag có format là ‘corctf{‘) và ta biết $n$ là bội của $p$ nên dùng coppersmith ta dễ dàng tính được $a$, có $a$ thì mọi chuyện gần như đã xong
Solution
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
from sage.all import *
from Crypto.Util.number import *
fbits = 375
n = 97915144495462666300795364589570761584322186881492143950078938328867290046424857019504657598883431857075772605985768551863478086544857915637724181292135280539943713583281151707224031808445390796342632369109562433275679473233398168787639940620683354458292117457239552762694657810883738834935391913698852811737
ct = 20363336204536918055183609604474634074539942561101208682977506918349108499764147141944713060658857301108876346227077713201766486360148051069618774935469969057808945271860025712869868421279488925632657486125211168314387620225601572070169746014988350688548088791906161773656057212229972967244998930356157725393
Gx, Gy = (3115938227771961657567351113281194074601897467086373590156577019504528350118731801249444974253028485083440228959842232653488953448859690520619223338133881, 2665631524518629436093690344927156713668794128141943350227439039472817541262750706395352700109556004195261826476428128993836186741129487842876154876730189)
a_high_bit = bytes_to_long('corctf{'.encode()) << (125 - 55)
P = PolynomialRing(Zmod(n), "x"); x = P.gen()
f = (3*Gx**2 + a_high_bit + x)**2 - 12 * Gx*Gy**2
a_low_bit = f.small_roots(X=2**70, beta=0.49)[0]
a = a_high_bit + a_low_bit
p = gcd(ZZ(f(a_low_bit)), n)
q = n//p
assert isPrime(p) and isPrime(q)
b = (Gy**2 - Gx**3 - a*Gx)%p
c = pow(ct, inverse(0x10001, (p - 1)*(q - 1)), n) >> (512 - 125)
flag = (int(a) << (2*125)) | (int(b) << 125) | int(c)
print(f'[+] Flag: {long_to_bytes(flag)}')
Flag:
corctf{you_have_conquered_the_order_of_three!!}
corrupted-curves+ (15 solves, 281 points)
Description
ok, no more being picky.
nc be.ax 31132Attachments
corruptedcurvesplus.py
Challenge overview
Sau khi giải bài corrupted-curves+ thì mình thấy lời giải có thể dùng cho bài corrupted-curves được luôn, nên mình sẽ chỉ trình bày cách tổng quát
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
from secrets import randbits
from Crypto.Util.number import getPrime
from random import randrange
def square_root(a, p):
if legendre_symbol(a, p) != 1:
return 0
elif a == 0:
return 0
elif p == 2:
return 0
elif p % 4 == 3:
return pow(a, (p + 1) // 4, p)
s = p - 1
e = 0
while s % 2 == 0:
s //= 2
e += 1
n = 2
while legendre_symbol(n, p) != -1:
n += 1
x = pow(a, (s + 1) // 2, p)
b = pow(a, s, p)
g = pow(n, s, p)
r = e
while True:
t = b
m = 0
for m in range(r):
if t == 1:
break
t = pow(t, 2, p)
if m == 0:
return x
gs = pow(g, 2 ** (r - m - 1), p)
g = (gs * gs) % p
x = (x * gs) % p
b = (b * g) % p
r = m
def legendre_symbol(a, p):
ls = pow(a, (p - 1) // 2, p)
return -1 if ls == p - 1 else ls
class EllipticCurve:
def __init__(self, p, a, b):
self.a = a
self.b = b
self.p = p
if not self.check_curve():
raise Exception("Not an elliptic curve!")
def check_curve(self):
discrim = -16 * (4*pow(self.a, 3) + 27*pow(self.b, 2))
if discrim % self.p:
return 1
return 0
def lift_x(self, px):
y2 = (pow(px, 3) + self.a*px + self.b) % self.p
py = square_root(y2, self.p)
if py == 0:
raise Exception("No point on elliptic curve.")
return py
with open("flag.txt", "rb") as f:
flag = f.read()
flag = int.from_bytes(flag, 'big')
print("Generating parameters...")
while True:
p = getPrime(512)
a, b = randbits(384), randbits(384)
try:
E = EllipticCurve(p, a, b)
fy = E.lift_x(flag)
print(f"p = {p}")
print(f"flag y = {fy}")
break
except:
continue
checked = set()
count = 0
while count < 2022:
x = randrange(2, p)
if int(x) in checked or x < 2**384 or abs(x - p) < 2**384:
print(">:(")
continue
try:
e = randbits(48)
print(f"e = {e}")
E = EllipticCurve(p, a^e, b^e)
py = E.lift_x(x)
checked.add(x)
print(f"x = {x}")
print(f"y = {py}")
count += 1
except:
print(":(")
more = input("more> ")
if more.strip() == "no":
break
print("bye!")
Ý tưởng chung của 2 bài là, đầu tiên sinh bộ ($a, b, p$: prime) (trong đó ta chỉ biết $p$) dùng làm tham số cho EllipticCurve sao cho có 1 điểm nào đó thuộc Curve có tọa độ $x$ đúng bằng flag. Sau đó mình được biết các bộ $(x, y, e)$ thuộc “fake curve” (bài đầu thì mình được chọn $x$ còn bài sau thì $x$ được sinh random bởi server)
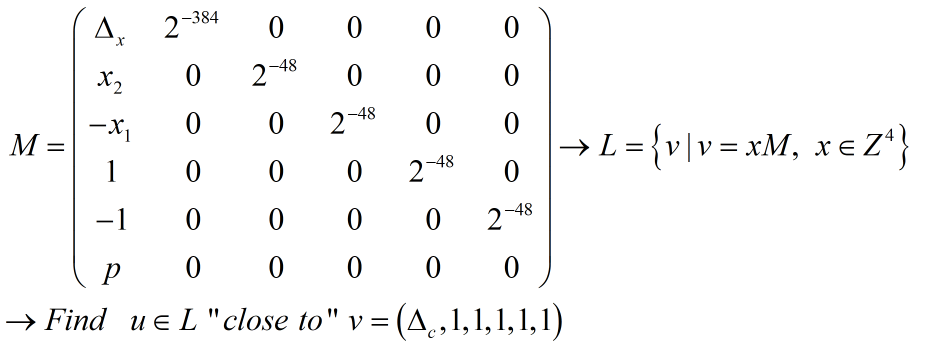
Ta thử biến đổi một chút
Vậy ý tưởng đã rõ ràng… Closest vector problem! ta sẽ tìm được a
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# http://mslc.ctf.su/wp/plaidctf-2016-sexec-crypto-300/
def babai_cvp(B, target):
B = B.LLL(delta=0.75)
G = B.gram_schmidt()[0]
small = target
for i in reversed(range(B.nrows())):
c = ((small * G[i]) / (G[i] * G[i])).round()
small -= c * B[i]
return target - small
mt = [
[deltax , QQ(1/2^384), 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ],
[x2 , 0 , QQ(1/2^48), 0 , 0 , 0 ],
[-x1 , 0 , 0 , QQ(1/2^48) , 0 , 0 ],
[ 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , QQ(1/2^48) , 0 ],
[-1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , QQ(1/2^48)],
[p , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ]
]
Basis = Matrix(QQ, mt)
cvp = babai_cvp(Basis, vector(QQ, [deltac, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]))
a = cvp[1] * 2^384
có $a$ rồi thừ mọi thứ dường như đã xong!
Solution
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
from Crypto.Util.number import *
p = 8223087986789035280051866940918282589719354860093319142129744296731295808879996333266655411090480291607568627486984163110794323450383260848298699322320393
fy = 5786965130631085576357593379746542211664496159572355991419185759634308266873774117908311187388012782703794713363367005200797504590199279126170683167985242
a = 3374447228755894062916771368749844037744742735467498296234442893155156299919677947547660966475084776111730207930850
b = 26490460255783524249701599340680356598934425315393006951112459329131256011011815322899216579106058767950117880792620
P.<x> = PolynomialRing(GF(p))
f = x^3 + a*x + b - fy^2
for rt, _ in f.roots():
flag = long_to_bytes(int(rt))
if b'corctf{' in flag:
print(f'[+] Flag: {flag}')
Flag:
corctf{cr4ftin6_f3as1ble_brut3s_unt1l_y0u_mak3_it!}